Nanotechnology for environment
Nanotechnology for energy and environment
Nanotechnology for energy and environment
The global energy and environmental situation has spurred increased focus on regenerative and environmentally friendly sources of energy. Nanotechnology is foreseen to play an important role in the development of new, efficient methods for eg H2 storage, CO2 capture and energy convertion.
The understanding and design of catalysts on the nanometerscale is of crucial importance to this field since materials may attain new properties at this level. Nanocatalysts may be single particles, aggregated particles or porous materials. In addition to carachterisation of the nanoparticles / nanomaterials themselves, one needs to understand the fundamental prosesses that take place when they are utilized as catalysts.
Some examples of research within nanotechnology for energy and environment at NTNU are given below.
Adsorbate-induced segregation in a PdAg membrane model system
Adsorbate-induced segregation in a PdAg membrane model system
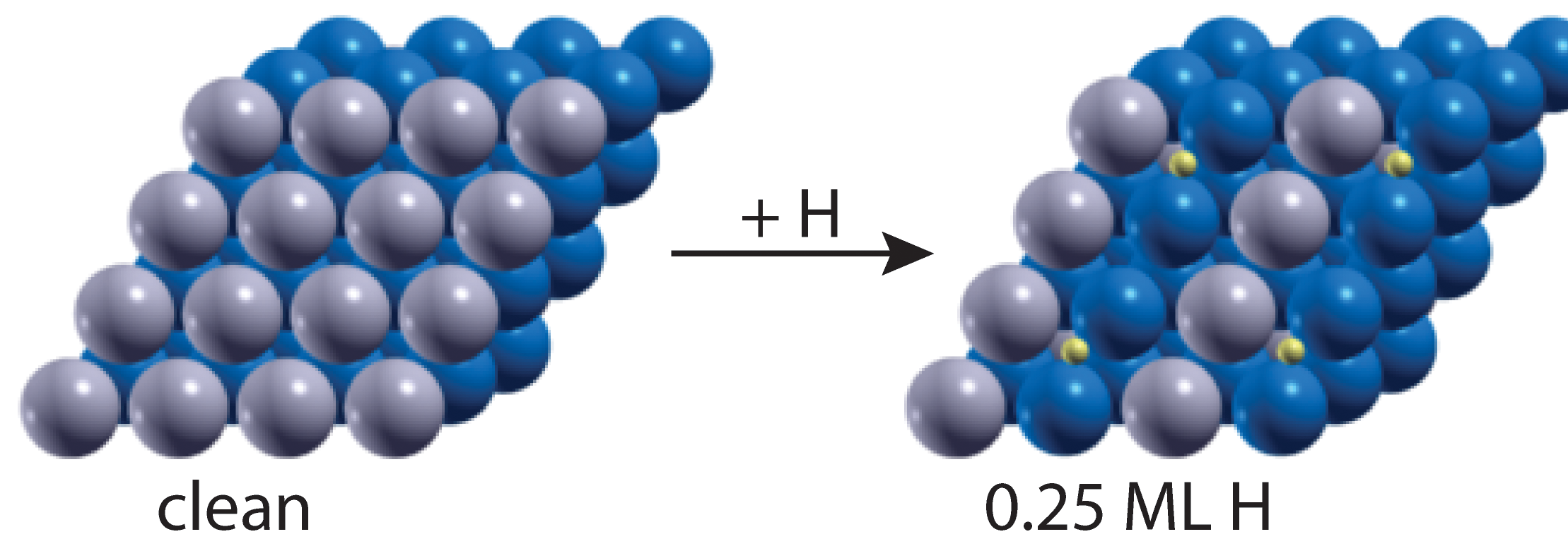 Segregation effects of a reactive environment on the (surface) structure and composition of PdAg membranes have been simulated by calculations of the electron structure of PdAg crystals provide a better understanding of how the adsorption of H2, CO or O2 on the surface is affected by the distribution between Pd and Ag in the topmost atomic layer and vice versa. Read more about adsorbate-induced segretation in a PdAg membrane model system...
Segregation effects of a reactive environment on the (surface) structure and composition of PdAg membranes have been simulated by calculations of the electron structure of PdAg crystals provide a better understanding of how the adsorption of H2, CO or O2 on the surface is affected by the distribution between Pd and Ag in the topmost atomic layer and vice versa. Read more about adsorbate-induced segretation in a PdAg membrane model system...
Nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C synthesized by a modified sol-gel method
Nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C synthesized by a modified sol-gel method
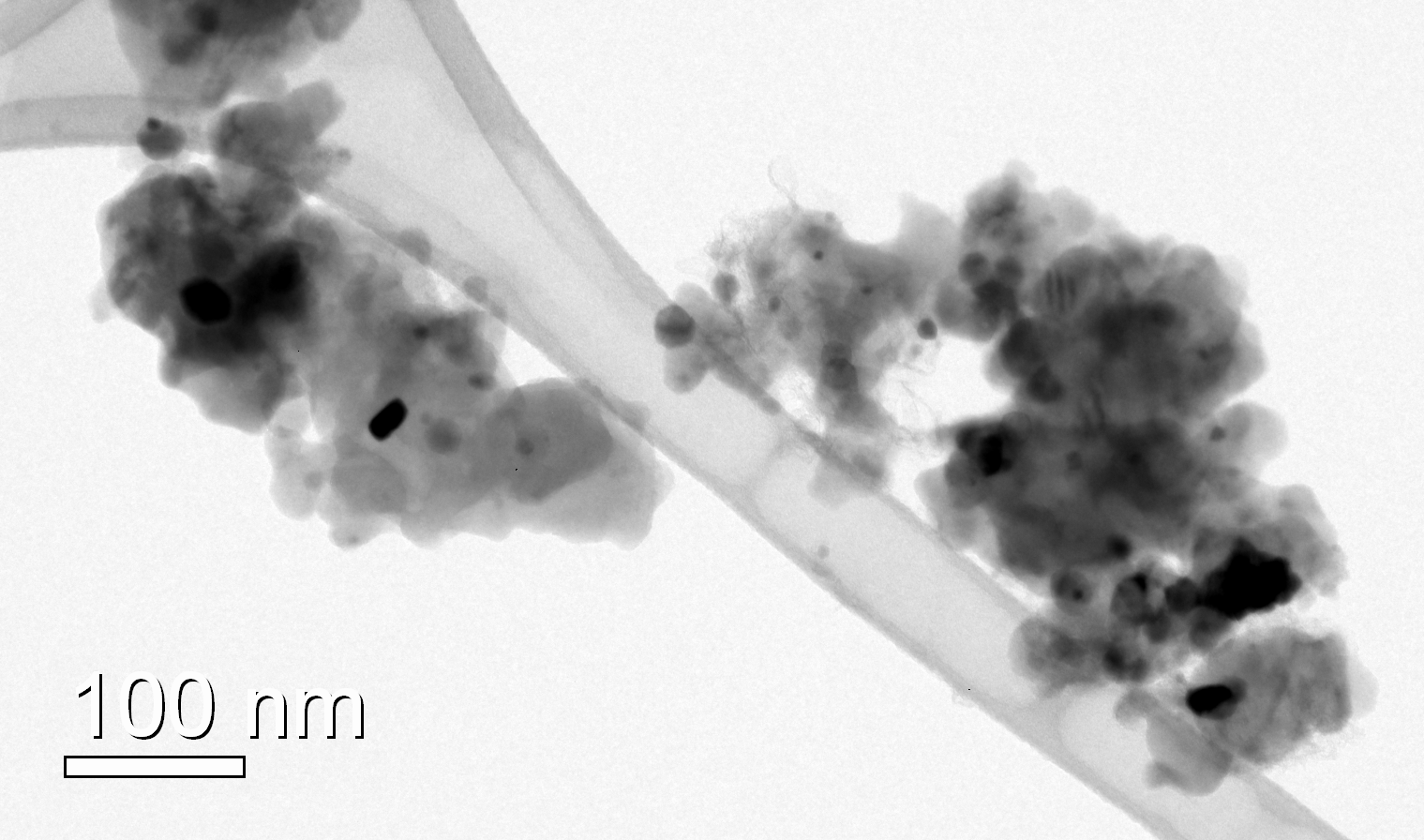 Li2FeSiO4/C composites used as cathode materials in Li-ion batteries have been synthesized by a modified sol-gel process. The process is water-based and uses environmentally friendly precursors. Read more about Nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C...
Li2FeSiO4/C composites used as cathode materials in Li-ion batteries have been synthesized by a modified sol-gel process. The process is water-based and uses environmentally friendly precursors. Read more about Nanostructured Li2FeSiO4/C...