WP3A: Development of cortical circuits for space and memory - The Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience
WP3A: Development of cortical circuits for space and memory
About
Motivation
Brain functions are supported by a variety of cell types that arise mainly during development (P3). The HPC-EC region is perfect for determining how circuit development depends on transient cell populations (such as Cajal-Retzius (CR) cells, which have prolonged survival in HPC), specific transcription factors (TFs), the timing of neurogenesis, and their relation to specific HPC-EC-dependent behaviours (memory, navigation).
Aims
We will exploit these qualities to unravel mechanisms guiding the formation of cortical networks:
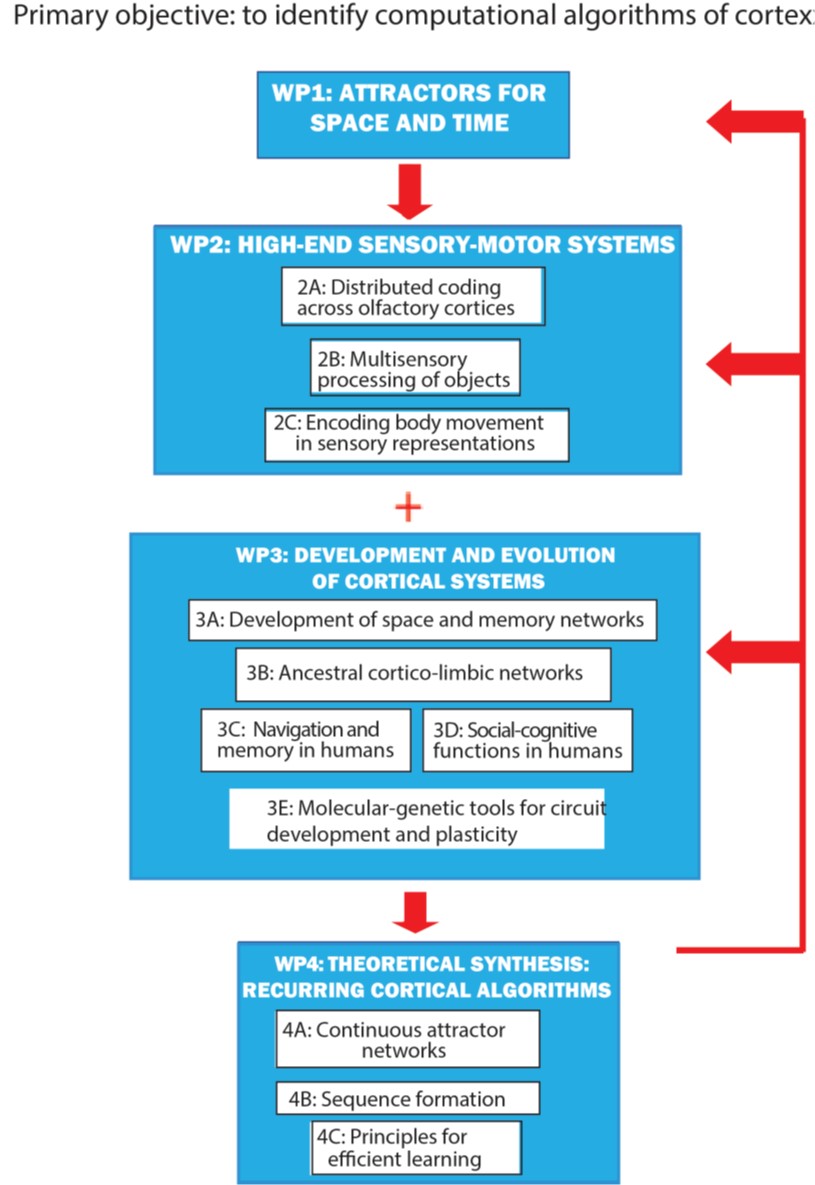
- 3.1 Uncover the contribution of CR cells to the maturation of the HPC network and function (P3)
- 3.2 Determine how changes in the expression of specific transcription factors at distinct developmental stages influence maturation, integration and function of HPC or MEC cells (P3)
- 3.3 Investigate whether the date of birth of entorhinal grid cells determines their integration in the circuit and the emergence of CAN architecture (P3,P1)
Implementation
With genetic tools, we shall ablate CR cells at early stages of postnatal development and then record with Neuropixels probes in HPC while mice learn HPC-dependent tasks, at young or adult age.
Using dimensionality reduction approaches we will determine the impact of CR cells on population dynamics and test if CR survival optimizes specific computations, e.g. storage capacity (WP4C).
Effects on local computation will also be determined by removing developmentally regulated TFs with expression in HPC-EC cells (e.g. Ctip2 in MEC stellate cells, with CK).
We will test with Neuropixels and miniscopes if isochronic grid cells (born on the same day) are preferentially integrated into the same grid module, with properties of a CAN (WP1,5AC; P1).